Animation- the art of bringing still images to life, with movement through a sequence of illustrations, models, or digital renderings – occupies an important niche in storytelling and visual communication, thrilling people everywhere, from movies, television, and games to commercials. An animator can do wonders by adjusting keyframes, timing, and spacing to make it appear in motion-think, from playful cartoons to lifelike CGI characters.
Animation is versatile because it crosses all lines of industries and helps explain difficult notions in an entertaining, educative, and engaging way. Its use in modern media underscores how animation transforms abstract ideas into memorable visual experiences.

Bring your stories to life with Ice n Fire Media’s Video Creation services! From concept to completion, we craft videos that captivate and inspire. Explore our services today at IcenFire Media!
What is Animation?
Animation refers to the perception of movement by a sequence of static frames or pictures viewed quickly. A series of frames demonstrate a flow of movement. If played in a loop, they could give the impression that movement was occurring. Animation is designed according to the principles of such things as keyframes, which are points that define where a movement starts and stops, tweening to fill in the frames showing moving objects between those points, timing to control speed, and spacing to observe the distance between objects. All these techniques make animations appear real and fluid.
Animation is an art form that grew from the original hand-drawn sequences of early cinema to the dominance of modern media using digital techniques. The most common forms are traditional 2D animation, where characters live on a two-dimensional plane; 3D animation, with digital models and depth; stop-motion, where objects take their life by being photographed frame-by-frame; and digital animation, which produces scenes using computer software.
Animation is important in various disciplines, such as entertainment, gaming, advertising, education, and web design. Its wide range of applications makes animators’ use significantly broad—they use animation to create funny characterizations, describe complicated ideas, and transport audiences to exciting worlds.
Animation refers to bringing something alive from an inanimate object or drawing, giving it the illusion of moving based on a sequence of images or frames. The animation is basically constructed from several very simple principles:
- Keyframes: Keyframes determine the starting and end positions of some movements. So basically, key frames can be regarded as “anchors” of animation.
- Tweening: This is the process of creating intermediary frames between the two extreme frames. These help in the transitions.
- Time: It determines how fast the objects move to create a sense of speed for the animation itself and in case a fast-timed or slow-motion option is chosen.
- Space: It defines the distance between objects in one frame, affecting the visual flow as well as motion.
Together, these two principles result in lifelike engaging animations that attract the attention of a person and bring meaningful experiences.
Types of Animation
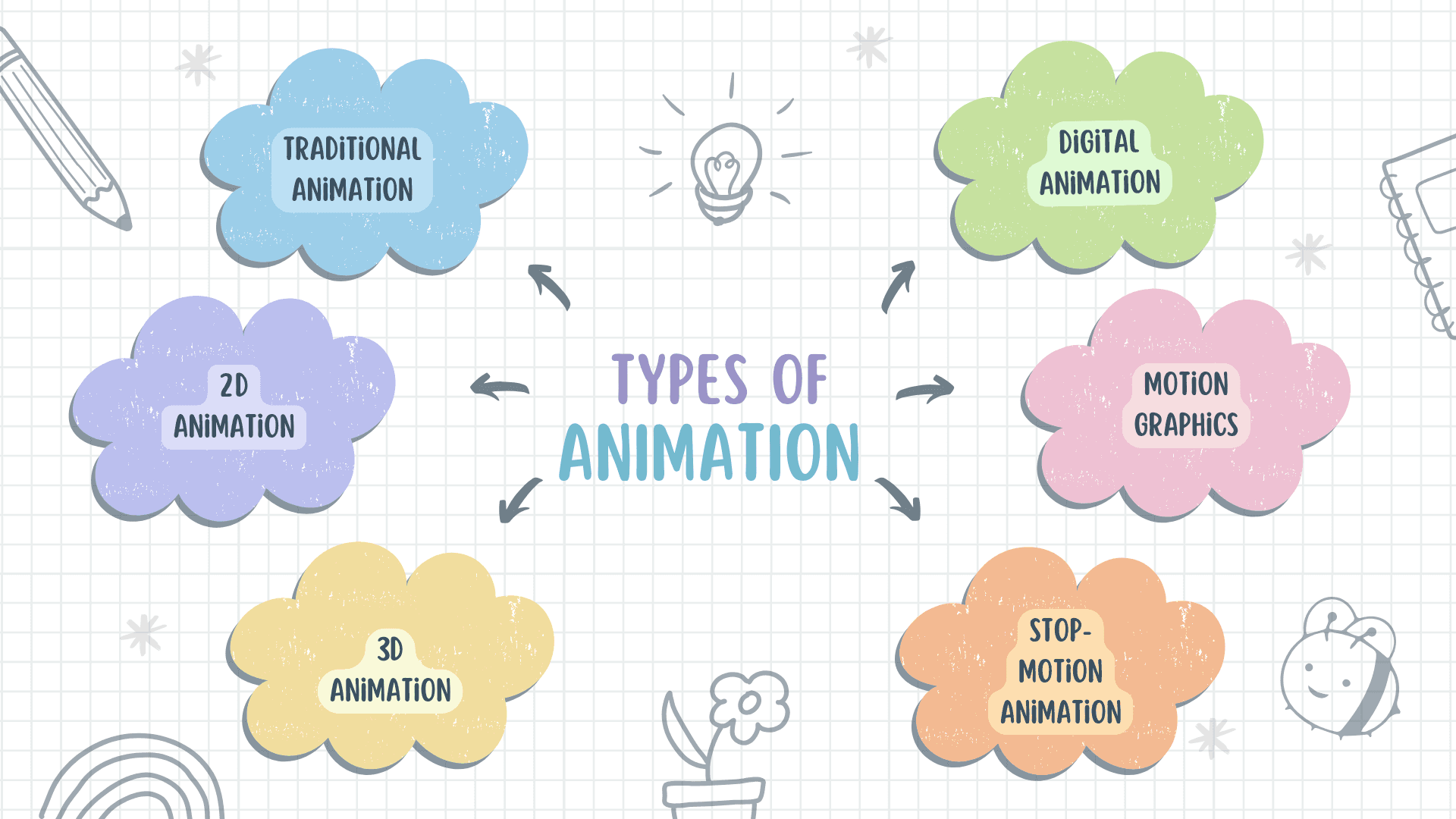
Many styles and techniques come with animation, bringing a unique flavor to visual storytelling. Here is a glimpse of some of the most popular types of animation:
Traditional Animation
The traditional type, also known as hand-drawn or cell animation, dates back to the oldest forms. In this type, every frame is hand-drawn, and when put together in a sequence, these drawings create an illusion of movement. This technique was employed frequently in the initial Disney movies, like Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs and Sleeping Beauty. Being labor-intensive, traditional animation has a unique style and grace with smooth-drawn movements and dramatic character designs. Some modern creators still use this technique for its old-school charm and artistic integrity.
2D Animation
Movement, in 2D animation, is created in a two-dimensional plane. Characters and objects are only defined to have height and width but do not extend any deeper. Most 2D animation is done digitally and forms the basis of most cartoons, advertisements, web series, and explainer videos. Software like Adobe Animate and Toon Boom Harmony have flattened the process of 2D animation, making it faster and more accessible to a broader audience compared to hand-drawn methods. This style can be identified because of its flat graphical appearance and will be best suited for those projects that might require interesting visuals but no excessive depth.
3D Animation
3D animation gives a piece a third dimension: depth, which opens up possibilities for more realistic, lifelike movements of characters and environments. Characters and environments are created as 3D models that can be rotated and manipulated inside virtual space. It is mostly used in CGI films, video games, and VR experiences. For example, in movies such as Toy Story and Frozen, 3D animation can be seen creating complex immersive environments. It can be quite resource-intensive, but 3D animation also allows the animators to create deep, realistic lighting and shadows combined with depth-giving textures, so it, in many ways, raises the stakes for animated storytelling.
Stop-Motion Animation
Stop-motion animation is a process where objects, usually figures of clay, puppets, or even the everyday objects of modern life, are photographed slightly differently in each frame. These frames, when played back in sequence, create the illusion of motion. Classic examples include Wallace and Gromit and The Nightmare Before Christmas. Stop-motion is unique in its tactile quality; the slight imperfections in each frame are what add a certain character’s homemade beauty. Though time-consuming to produce, stop-motion allows for many effects that could not be done using digital techniques.
Motion Graphics
Motion graphics are animated graphic designs, mostly in explainer videos, commercials, and multimedia presentations. This type of design favors movement to convey messages or pass information with images or text where shapes and icons help in illustrating the message. Motion graphics do not aim to tell a sophisticated story with characters but somehow make complex ideas more presentable and elegant in a presentation or user interface. Typical software for producing motion graphics includes Adobe After Effects, among others, which produces motion graphics, such as text animation, transitional screens, and other visual effects.
Digital Animation
Mainly, 2D and 3D animation in digital animation are created more with the help of software used for the creation, rendering, and manipulation of animations. Specialized forms in this category include film character animation, web animations, and app interfaces. Flexibility is the main advantage of digital animation for creators, as it allows for quick cuts, ease of reuse, and a variety of effects that can’t be replicated by standard methods. This is why it’s highly used across practically all current media platforms-from digital advertising material to social media, where short, interesting content is particularly crucial.
Different styles of animation have varied methods of delivery and are chosen based on the project’s objective, target group, or the resources already in hand. The magic of traditional animation, the realism of 3D, or the art of stop-motion ensures whatever style of animation is used creates infinite possibilities in storytelling and creativity.
Also Read:
- Top 10 Best Video Editing Apps
- Top 10 Best Video Editing Services in USA
- How to Create Great PowerPoint Presentations? Step by Step Guide
Using PowerPoint Animation
Animation can be done not only in films and TV shows but also in presentations such as when using Microsoft PowerPoint, in which the animation effects may make the information more interesting and easier to digest.
How to animate in PowerPoint:
- Adding animations to text, shapes, and objects: You simply need to pick up the object you want to animate, go to the “Animations” tab, and choose an effect that could be “Fade,” “Fly-In,” or “Bounce.”.
- Animation Speed, Sequence, and Delay: PowerPoint also allows you to modify animation speed and sequence, and even add a delay if you want to tightly control the appearance and interaction of objects.
- Transitions Between Slides: There are effects that move over the transition from one slide to another. Applying transitions, such as “Morph” or “Push,” can make a presentation seem more fluid and professional.
Animation Software
Animation software has revolutionized the creative landscape to change the face of the world. Artists and designers can now make high-quality animations with efficiency and precision. Many animation programs are tailor-made to suit the various levels of skill, techniques, and end goals.
Here is a glimpse of popular animation software that contributes to the animation process:
Adobe Animate
Adobe Animate is versatile 2D animation software used to produce an enormous number of animations for websites, videos, and games. It is part of the Adobe Creative Cloud suite, where a user can create animations, vector graphics, and interactive content. This makes Adobe Animate pretty popular in the field of web animations, particularly because it can support HTML5, SVG, and WebGL to create responsive, interactive animations for online media. It has a very friendly interface and integrates with other Adobe programs, which makes it ideal for beginners and experienced animators.
Blender
Blender is free and open-source 3D creation software used to create 3D models, visual effects, and animations. With its advanced modeling, sculpting, texturing, and rendering capabilities, Blender is the best suited for the various industries of animators for game development and film. Some of the tools they have include character animation and fluid simulations, realistic lighting, and shadows. It also supports 2D and 3D animation using the Grease Pencil feature, so it is pretty versatile. In spite of all the technicality, Blender has a good community and enough tutorials around, which make it easy for beginners to learn.
Autodesk Maya
Then, there is the more familiar and respected software for 3D animation, Autodesk Maya, which is from the film, television, and game design industry’s group. The software is appreciated for its high-end capabilities: complex character animation, 3D modeling, motion graphics, and rendering. It often deals with large projects containing realistic animations and visual effects, especially in blockbuster films and AAA video games. With the steep learning curve, this software is certainly not for amateur animators but can still prove useful to studios-they are extremely comprehensive, well-standardized, and represent the very best of industry standards.
Toon Boom Harmony
Toon Boom Harmony is professional 2D animation software that is robust, versatile, and widespread among professionals and hobbyists alike working in TV animation, films, and game development-a set of frame-by-frame and rig-based tools. Harmony may be smoothly integrated into the process, supporting both bitmap and vector-based animation, as well as powerful compositing tools. Especially cherished for professionals, Toon Boom Harmony uses many of the studio’s professional features. Its key features help in producing traditional and cut-out styles of animation. Especially useful for projects that require a quality turn with a high production-ready finish.
Synfig Studio
Synfig Studio is a freeware, open-source 2D animation software that is perfect for producing quality animations with frame-by-frame-less-fuss adjustments. It establishes vector-based animation along with tweening to perform automatic transitions between frames for efficient animation production with smooth and fluid movements. Synfig is user-friendly but has advanced features like gradient shading, bone rigging, morphing, and so on.
Creating Your Own Animation
Animation can be a very rewarding process. This will help you come up with characters, tell stories, and discover attractive visuals. Beginner or seasoned animator, coming up with animation is a journey that helps you bring alive the life of 2D characters, stories, and visual effects. Here’s a step-by-step guide in the animation production to get you ready to go for the ride:
Planning and Concept Development
The first step in any animation project is planning. This includes developing the concept, determining who the characters are, and what the storyline is.
- Storyboarding: A storyboard is an illustration that is essentially a visual plan where you draw out every scene and action sequence, almost charting the final animation. It helps you to see how each shot will unfold-timewise and in terms of composition.
- Scriptwriting: If your animation contains dialogue or narration, a script will be required to structure the story and guide the visuals. This lends context to scenes and helps more significantly with flow.
- Character Design: Character sketches and think about every character’s personality, movements, and unique features. Characters need to be expressive and fit within the realistic or fantastic tone of the story.
Sketching and Rough Drafting
With the concept in mind, start making rough animation drafts.
- Rough Sketches: Start by doing simple sketches of characters, backgrounds, and key scenes. The drafts help visualize the movement, posture, and composition of the scene.
- Keyframes: This is used to point out the important movements’ beginning and end. These are basically frames wherein the key or main poses and actions of the characters occur, and these will be what forms the basis of your whole animation.
Inking and Outlining
Inking helps complete clear outlines of your sketches on an overlay sheet. This helps add clarity and detail to each of your characters and scenes. Adding clean outlines ensures your animation is clean and clear before carrying on to the next steps.
- Line Art: This is tracing over rough sketches with smooth lines and keeping things clean and fully understood. This is especially important for 2D animation, or your animation will be a mess.
- Detailing: Add such face expressions, textures, and finer details to characters and backgrounds. This step gives personality and depth to your design.
Color and Shading
After completion of the outlines, you are ready to begin color and shading on characters and backgrounds.
- Base Colors: Applying flat colors to set the general look of a character or object and attributing a color scheme according to the mood of the animation will do.
- Shading and Highlights: Shading and highlights will be implemented on the 3D and highly detailed 2D animations to create depth and a better resemblance to reality while sometimes adding drama or highlighting illumination in many other scenes.
Animation
Animating is where your project comes to life. It varies depending on the type of animation, whether it be 2D, 3D, or stop-motion, but essentially all the processes are similar.
- Tweening: Tweening generates intermediate frames between the keyframes, producing smooth transitions in the movements. It can be done either by hand or by the software itself.
- Rigging (for 3D Animation): Rigging with 3D characters lets one set up a “skeleton” to help in controlling their movements. This allows for lifelike and smooth animation of limbs, facial expressions, and other parts of the body.
- Timing and spacing: This is equivalent to the speed of movement and spacing, which defines the positioning between frames. You can use these elements to give your animation some fast-motion or slow-motion effects that accentuate the flow of action.
- Backgrounds and Effects: Majorly, the backgrounds, and effects keep the place and make the environment and help bring it up.
- Background Designing: Create and include backgrounds that suit the ‘tone of the scene’ and ‘setting.’ Backgrounds can be simple or detailed depending on your style or purpose.
- Special Effects: In addition to shadows, reflections, particle effects, and lighting, add more depth to the animation. Pretty much all animation platforms come with built-in effects, which, more often than not, are easily customizable for the project that you’re working on.
Rendering and Exporting
Rendering simply takes the last output, whereby you combine all your frames, colors, and effects into a seamless video file.
- Rendering Settings: Before doing the rendering, make sure that you have set the resolution, frame rate, as well as file format. High-resolution settings are advisable for professional projects but may be good enough for smaller web animations at lower resolutions.
- Exporting: Once you have completed your animation, then export it in a suitable format depending on how you want to use it: social media, website, film. Suitable formats usually would be MP4, GIF, AVI, etc.
Applications of Animation
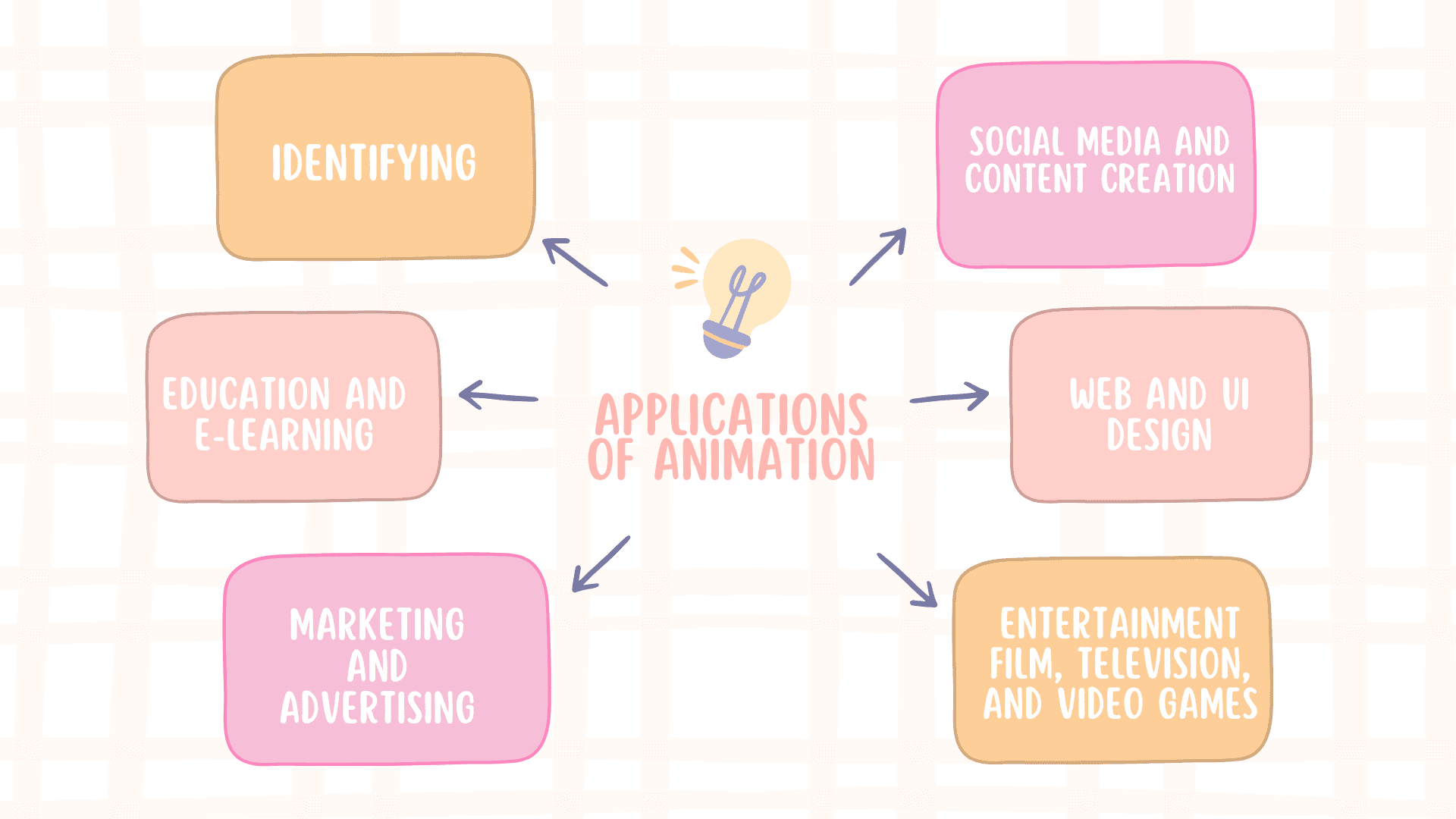
Animation is a versatile tool applied in various applications: entertainment and education, marketing, and medicine. Let’s begin with an overview of the most important areas where animation plays a highly significant role:
Entertainment: Film, Television, and Video Games
The entertainment industry will probably be the most identifiable application of animation. The imaginative animation has captured both young and adult audiences in animated movies, television shows, and games.
- Film and TV: Animation enables filmmakers to tell dramatic stories and create fantastic worlds that would be unfilmable in some sense if not for animation. From the classic 2D works – such as Looney Tunes – to the revolutionary 3D movies like Toy Story or Avatar, animation brings stories to life on film.
- Video Games: Animations have become very important in the production of video game characters and scenes. 2D and 3D animation, smooth character movements, and lifelike interactions in the game improve the design of game worlds.
Education and E-Learning
Animation has rapidly turned into a tool for education to improve understanding of complex concepts with fun and accessibility.
- Instructional Videos: Educational videos are usually rich in animated sequences meant to explain subjects like math, science, or history. Such animated visuals help render complex concepts understandable for the viewers.
- Interactive Learning: Educational apps often use animated elements in a lesson to encourage interaction and make it fun. With animation in lessons, it can be made visually appealing and accessible to all age groups to retain.
Marketing and Advertising
Marketers tend to use animation in disruptive advertisements and a brand narrative that resonates with the target audience.
- Advertisements: Compared to the competition, animated advertisements manage to grab the attention of the product’s message through motion graphics and characters.
- Explainer Videos: Many brands have utilized animation in explainer videos to describe their services or products enthusiastically and in greater detail. Animated logos and characters further make brand identities memorable and accessible.
Web and UI Design
Animation enhances the UX of a website or application.
- Micro-Interactions: Micro-interactions are small animations that navigate from one place to another, from a link to another, or even from a loading indicator for the system. They are feedback elements for users, guide them, and make them experience things intuitively.
- Website Graphics: The use of animations in websites has been encouraged to tell stories. This is achieved when content is brought to life, making it look more attractive through animated infographics, parallax scrolling, and dynamic background elements.
Social Media and Content Creation
Animations are fast gaining popularity because of the highly engaging format and with significant opportunities to go viral.
- Social Media Posts: Most brands have used the ‘short animated videos” to promote themselves on the social networking site. These videos are shareable, and thus help in ‘reaching more people”.
- GIFs and Stickers: Animation constitutes much of the material used in social messaging-Generally, GIFs and stickers constitute a significant proportion of the content used in social messaging. Such short animations have become a popular choice for fast and playful communication, entertaining and expressive in nature.
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
Animation is an integral part of the development of immersive experiences with a focus on interaction in the growing fields of AR and VR.
- Gaming and Simulation: It brings out interesting, interactive environments, be it for gaming or practical simulations.
- Training and Education: Virtual Reality helps the user to develop their skills in a virtual environment. Sometimes, for a pilot, it would be through a flight simulator. Other times, students in medicine could simulate surgery. Animation makes these environments look all the more realistic and deepens the curve of learning.
Conclusion
Animation is an excellent means of communication, entertainment, and discovery. Techniques from static 2D cartoons to realistic 3D models continue to evolve with technology and new software. Delve into the ever-changing art form of animation as you learn about the types, principles, and applications of animation. Animation is limitless: You can use it for something personal, add a to-your-presentations educational vibe, or make it solely professional. So, enter the world of animation and see what kind of creative experimentation you might come up with – as you very well know where your imagination can lead you!

